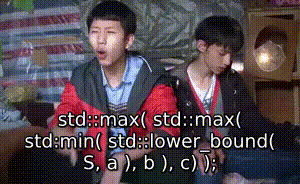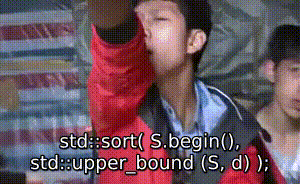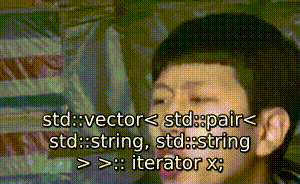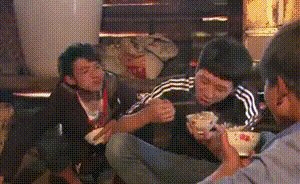序 此文为其他文章的代码部分:
🥵硬啃-Machine-Learning
也提供了 notebook 形式: 代码地址
数据预处理方法 标准化-均值移除 import numpy as npimport sklearn.preprocessing as spraw_samples = np.array([ [3.0 , -1.0 , 2.0 ],\ [0.0 , 4.0 , 3.0 ], \ [1.0 , -4.0 , 2.0 ]]\ ) print (raw_samples.mean(axis=0 ))print (raw_samples.std(axis=0 ))std_samples = raw_samples.copy() for col in std_samples.T: col_mean = col.mean() col_std = col.std() col -= col_mean col /= col_std print (std_samples.mean(axis=0 ))print (std_samples.std(axis=0 ))std_samples = sp.scale(raw_samples) print (std_samples.mean(axis=0 ))print (std_samples.std(axis=0 ))
[ 1.33333333 -0.33333333 2.33333333]
[1.24721913 3.29983165 0.47140452]
[ 5.55111512e-17 0.00000000e+00 -2.96059473e-16]
[1. 1. 1.]
[ 5.55111512e-17 0.00000000e+00 -2.96059473e-16]
[1. 1. 1.]
范围缩放 import numpy as npimport sklearn.preprocessing as spraw_samples = np.array([ [1.0 , 2.0 , 3.0 ],\ [4.0 , 5.0 , 6.0 ],\ [7.0 , 8.0 , 9.0 ]]).astype("float64" ) mms_samples = raw_samples.copy() for col in mms_samples.T: col_min = col.min () col_max = col.max () col -= col_min col /= (col_max - col_min) print (mms_samples)mms_samples = sp.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 ))\ .fit_transform(raw_samples) print (mms_samples)
[[0. 0. 0. ]
[0.5 0.5 0.5]
[1. 1. 1. ]]
[[0. 0. 0. ]
[0.5 0.5 0.5]
[1. 1. 1. ]]
归一化 import numpy as npimport sklearn.preprocessing as spraw_samples = np.array([ [10.0 , 20.0 , 5.0 ],\ [8.0 , 10.0 , 1.0 ]]) nor_samples = raw_samples.copy() for row in nor_samples: row /= abs (row).sum () print (nor_samples) nor_samples = sp.normalize(raw_samples.copy(), norm='l1' ) print (nor_samples)
[[0.28571429 0.57142857 0.14285714]
[0.42105263 0.52631579 0.05263158]]
[[0.28571429 0.57142857 0.14285714]
[0.42105263 0.52631579 0.05263158]]
二值化 import numpy as npimport sklearn.preprocessing as spraw_samples = np.array([[65.5 , 89.0 , 73.0 ],\ [55.0 , 99.0 , 98.5 ],\ [45.0 , 22.5 , 60.0 ]]) bin_samples = raw_samples.copy() mask1 = bin_samples < 60 print (mask1)mask2 = bin_samples >= 60 bin_samples[mask1] = 0 print (bin_samples)bin_samples[mask2] = 1 print (bin_samples) bin_transformer = sp.Binarizer(threshold=60 - 1 ) bin_samples = bin_transformer.transform(raw_samples.copy()) print (bin_samples)
[[False False False]
[ True False False]
[ True True False]]
[[65.5 89. 73. ]
[ 0. 99. 98.5]
[ 0. 0. 60. ]]
[[1. 1. 1.]
[0. 1. 1.]
[0. 0. 1.]]
[[1. 1. 1.]
[0. 1. 1.]
[0. 0. 1.]]
独热编码示例 import numpy as npimport sklearn.preprocessing as spraw_samples = np.array([[1 , 3 , 2 ],\ [7 , 5 , 4 ],\ [1 , 8 , 6 ],\ [7 , 3 , 9 ]]) one_hot_encoder = sp.OneHotEncoder( sparse=False , dtype="int32" , categories="auto" ) oh_samples = one_hot_encoder.fit_transform(raw_samples.copy()) print (oh_samples)print (one_hot_encoder.inverse_transform(oh_samples))
[[1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0]
[0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0]
[0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1]]
[[1 3 2]
[7 5 4]
[1 8 6]
[7 3 9]]
标签编码 import numpy as npimport sklearn.preprocessing as spraw_samples = np.array(['audi' , 'ford' , 'audi' , 'bmw' , 'ford' , 'bmw' ]) lb_encoder = sp.LabelEncoder() lb_samples = lb_encoder.fit_transform(raw_samples.copy()) print (lb_samples)print (lb_encoder.inverse_transform(lb_samples))
[0 2 0 1 2 1]
['audi' 'ford' 'audi' 'bmw' 'ford' 'bmw']
基本问题 回归问题 线性回归 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as mpfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3dimport sklearn.preprocessing as sptrain_x = np.array([0.5 , 0.6 , 0.8 , 1.1 , 1.4 ]) train_y = np.array([5.0 , 5.5 , 6.0 , 6.8 , 7.0 ]) n_epochs = 30 l_rate = 0.01 epochs = [] losses = [] w0, w1 = [1 ], [1 ] for i in range (1 , n_epochs + 1 ): epochs.append(i) y = w0[-1 ] + w1[-1 ] * train_x loss = (((train_y - y)**2 ).sum ()) / 2 losses.append(loss) print ("%d: w0=%f, w1=%f, loss=%f" % (i, w0[-1 ], w1[-1 ], loss)) d0 = -(train_y - y).sum () d1 = -(train_x * (train_y - y)).sum () w0.append(w0[-1 ] - (d0 * l_rate)) w1.append(w1[-1 ] - (d1 * l_rate)) w0 = np.array(w0[:-1 ]) w1 = np.array(w1[:-1 ]) mp.figure("Losses" , facecolor="lightgray" ) mp.title("epoch" , fontsize=20 ) mp.ylabel("loss" , fontsize=14 ) mp.grid(linestyle=":" ) mp.plot(epochs, losses, c="blue" , label="loss" ) mp.legend() mp.tight_layout() pred_y = w0[-1 ] + w1[-1 ] * train_x mp.figure("Linear Regression" , facecolor="lightgray" ) mp.title("Linear Regression" , fontsize=20 ) mp.xlabel("x" , fontsize=14 ) mp.ylabel("y" , fontsize=14 ) mp.grid(linestyle=":" ) mp.scatter(train_x, train_y, c="blue" , label="Traing" ) mp.plot(train_x, pred_y, c="red" , label="Regression" ) mp.legend() arr1 = np.linspace(0 , 10 , 500 ) arr2 = np.linspace(0 , 3.5 , 500 ) grid_w0, grid_w1 = np.meshgrid(arr1, arr2) flat_w0, flat_w1 = grid_w0.ravel(), grid_w1.ravel() loss_metrix = train_y.reshape(-1 , 1 ) outer = np.outer(train_x, flat_w1) flat_loss = (((flat_w0 + outer - loss_metrix)**2 ).sum (axis=0 )) / 2 grid_loss = flat_loss.reshape(grid_w0.shape) mp.figure('Loss Function' ) ax = mp.axes(projection='3d' ) mp.title('Loss Function' , fontsize=14 ) ax.set_xlabel('w0' , fontsize=14 ) ax.set_ylabel('w1' , fontsize=14 ) ax.set_zlabel('loss' , fontsize=14 ) ax.plot_surface(grid_w0, grid_w1, grid_loss, rstride=10 , cstride=10 , cmap='jet' ) ax.plot(w0, w1, losses, 'o-' , c='orangered' , label='BGD' , zorder=5 ) mp.legend(loc='lower left' ) mp.show()
1: w0=1.000000, w1=1.000000, loss=44.175000
2: w0=1.209000, w1=1.190600, loss=36.538828
3: w0=1.399164, w1=1.363579, loss=30.231687
4: w0=1.572208, w1=1.520546, loss=25.022227
5: w0=1.729693, w1=1.662961, loss=20.719373
6: w0=1.873039, w1=1.792151, loss=17.165309
7: w0=2.003532, w1=1.909325, loss=14.229691
8: w0=2.122345, w1=2.015577, loss=11.804865
9: w0=2.230542, w1=2.111905, loss=9.801916
10: w0=2.329091, w1=2.199215, loss=8.147408
11: w0=2.418871, w1=2.278330, loss=6.780688
12: w0=2.500681, w1=2.349997, loss=5.651660
13: w0=2.575247, w1=2.414898, loss=4.718950
14: w0=2.643230, w1=2.473648, loss=3.948384
15: w0=2.705228, w1=2.526811, loss=3.311740
16: w0=2.761786, w1=2.574896, loss=2.785706
17: w0=2.813402, w1=2.618367, loss=2.351029
18: w0=2.860524, w1=2.657645, loss=1.991807
19: w0=2.903561, w1=2.693114, loss=1.694907
20: w0=2.942886, w1=2.725122, loss=1.449482
21: w0=2.978836, w1=2.753985, loss=1.246572
22: w0=3.011719, w1=2.779990, loss=1.078777
23: w0=3.041814, w1=2.803399, loss=0.939987
24: w0=3.069373, w1=2.824449, loss=0.825153
25: w0=3.094629, w1=2.843355, loss=0.730107
26: w0=3.117790, w1=2.860315, loss=0.651405
27: w0=3.139046, w1=2.875507, loss=0.586204
28: w0=3.158572, w1=2.889091, loss=0.532154
29: w0=3.176523, w1=2.901216, loss=0.487315
30: w0=3.193044, w1=2.912016, loss=0.450086
import numpy as npimport sklearn.linear_model as lm import sklearn.metrics as sm import matplotlib.pyplot as mptrain_x = np.array([[0.5 ], [0.6 ], [0.8 ], [1.1 ], [1.4 ]]) train_y = np.array([5.0 , 5.5 , 6.0 , 6.8 , 7.0 ]) line_model = lm.LinearRegression() line_model.fit(train_x, train_y) pred_y = line_model.predict(train_x) print ("coef_:" , line_model.coef_) print ("intercept_:" , line_model.intercept_) mp.figure('Linear Regression' , facecolor='lightgray' ) mp.title('Linear Regression' , fontsize=20 ) mp.xlabel('x' , fontsize=14 ) mp.ylabel('y' , fontsize=14 ) mp.tick_params(labelsize=10 ) mp.grid(linestyle=':' ) mp.scatter(train_x, train_y, c='blue' , alpha=0.8 , s=60 , label='Sample' ) mp.plot( train_x, pred_y, c='orangered' , label='Regression Line' ) mp.legend() mp.show()
coef_: [2.2189781]
intercept_: 4.107299270072994
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom sklearn import datasets, linear_model, model_selectionX, y = datasets.load_diabetes(return_X_y=True ) print (X.shape)print (X[0 ])X = X[:, np.newaxis, 2 ] X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split( X, y, test_size=0.33 ) model = linear_model.LinearRegression() model.fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = model.predict(X_test) plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color='black' ) plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color='blue' , linewidth=3 ) plt.show()
(442, 10)
[ 0.03807591 0.05068012 0.06169621 0.02187235 -0.0442235 -0.03482076
-0.04340085 -0.00259226 0.01990842 -0.01764613]
import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom datetime import datetimepumpkins = pd.read_csv('./_data_set/US-pumpkins.csv' ) pumpkins = pumpkins[pumpkins['Package' ].str .contains('bushel' , case =True , regex=True )] pumpkins = pumpkins.drop([ c for c in pumpkins.columns if c not in [ 'Package' , 'Variety' , 'City Name' , 'Month' , 'Low Price' , 'High Price' , 'Date' ] ], axis=1 ) price = (pumpkins['Low Price' ] + pumpkins['High Price' ]) / 2 new_pumpkins = pd.DataFrame({ 'Month' : pd.DatetimeIndex(pumpkins['Date' ]).month, 'DayOfYear' : pd.to_datetime(pumpkins['Date' ]).apply( lambda dt: (dt - datetime(dt.year, 1 , 1 )).days), 'Variety' : pumpkins['Variety' ], 'City' : pumpkins['City Name' ], 'Package' : pumpkins['Package' ], 'Low Price' : pumpkins['Low Price' ], 'High Price' : pumpkins['High Price' ], 'Price' : price }) new_pumpkins.loc[new_pumpkins['Package' ].str .contains('1 1/9' ), 'Price' ] = price / (1 + 1 / 9 ) new_pumpkins.loc[new_pumpkins['Package' ].str .contains('1/2' ), 'Price' ] = price / (1 / 2 ) plt.scatter(new_pumpkins.Price, new_pumpkins.Month) plt.xlabel('Price' ) plt.ylabel('Month' ) plt.show() new_pumpkins.groupby(['Month' ])['Price' ].mean().plot(kind='bar' ) plt.ylabel('Month' ) ax = None colors = ['red' , 'blue' , 'green' , 'yellow' ] for i, var in enumerate (new_pumpkins['Variety' ].unique()): ax = new_pumpkins[new_pumpkins['Variety' ] == var].plot.scatter('DayOfYear' , 'Price' , ax=ax, c=colors[i], label=var)
多项式回归 import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom datetime import datetimefrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_errorfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeaturesfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipelinepumpkins = pd.read_csv('./_data_set/US-pumpkins.csv' ) pumpkins = pumpkins[pumpkins['Package' ].str .contains('bushel' , case =True , regex=True )] pumpkins = pumpkins.drop([ c for c in pumpkins.columns if c not in [ 'Package' , 'Variety' , 'City Name' , 'Month' , 'Low Price' , 'High Price' , 'Date' ] ], axis=1 ) price = (pumpkins['Low Price' ] + pumpkins['High Price' ]) / 2 new_pumpkins = pd.DataFrame({ 'Month' : pd.DatetimeIndex(pumpkins['Date' ]).month, 'DayOfYear' : pd.to_datetime(pumpkins['Date' ]).apply( lambda dt: (dt - datetime(dt.year, 1 , 1 )).days), 'Variety' : pumpkins['Variety' ], 'City' : pumpkins['City Name' ], 'Package' : pumpkins['Package' ], 'Low Price' : pumpkins['Low Price' ], 'High Price' : pumpkins['High Price' ], 'Price' : price }) new_pumpkins.loc[new_pumpkins['Package' ].str .contains('1 1/9' ), 'Price' ] = price / 1.1 new_pumpkins.loc[new_pumpkins['Package' ].str .contains('1/2' ), 'Price' ] = price * 2 pie_pumpkins = new_pumpkins[new_pumpkins['Variety' ] == 'PIE TYPE' ] X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( pie_pumpkins['DayOfYear' ].to_numpy().reshape(-1 , 1 ), pie_pumpkins['Price' ], test_size=0.2 , random_state=0 ) pipeline = make_pipeline(PolynomialFeatures(2 ), LinearRegression()) pipeline.fit(X_train, y_train) pred = pipeline.predict(X_test) mse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, pred)) print (f'Mean error: {mse:3.3 } ({mse/np.mean(pred)*100 :3.3 } %)' )score = pipeline.score(X_train, y_train) print ('Model determination: ' , score)plt.scatter(X_test, y_test) plt.plot(sorted (X_test), pipeline.predict(sorted (X_test)))
Mean error: 2.73 (17.0%)
Model determination: 0.07639977655280084
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x19b75ee76d0>]
决策树-随机森林 决策树分类 import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib as mplfrom sklearn import treefrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scorefrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoderimport pydotplusmpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif' ] = ['simHei' ] mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus' ] = False iris_feature_E = 'sepal length' , 'sepal width' , 'petal length' , 'petal width' iris_feature = '花萼长度' , '花萼宽度' , '花瓣长度' , '花瓣宽度' iris_class = 'Iris-setosa' , 'Iris-versicolor' , 'Iris-virginica' path = './_data_set/iris_classification/iris.data' data = pd.read_csv(path, header=None ) x = data[list (range (4 ))] y = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(data[4 ]) x = x[[0 , 1 ]] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3 , random_state=1 ) model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy' ) model.fit(x_train, y_train) y_train_pred = model.predict(x_train) print ('训练集正确率:' , accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred))y_test_hat = model.predict(x_test) print ('测试集正确率:' , accuracy_score(y_test, y_test_hat))tree.export_graphviz(model, out_file='./_data_set/iris_classification/iris.dot' , feature_names=iris_feature_E[0 :2 ], class_names=iris_class, filled=True , rounded=True , special_characters=True ) dot_data = tree.export_graphviz(model, out_file=None , feature_names=iris_feature_E[0 :2 ], class_names=iris_class, filled=True , rounded=True , special_characters=True ) graph = pydotplus.graph_from_dot_data(dot_data) graph.write_pdf('./_data_set/iris_classification/iris.pdf' ) f = open ('./_data_set/iris_classification/iris.png' , 'wb' ) f.write(graph.create_png()) f.close() N, M = 50 , 50 x1_min, x2_min = x.min () x1_max, x2_max = x.max () t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, N) t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, M) x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2) x_show = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1 ) print (x_show.shape)print ('x_show = \n' , x_show)cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0' , '#FFA0A0' , '#A0A0FF' ]) cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g' , 'r' , 'b' ]) y_show_hat = model.predict(x_show) print (y_show_hat.shape)print (y_show_hat)y_show_hat = y_show_hat.reshape(x1.shape) print (y_show_hat)plt.figure(facecolor='w' ) plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_show_hat, cmap=cm_light, shading='auto' ) plt.scatter(x_test[0 ], x_test[1 ], c=y_test.ravel(), edgecolors='k' , s=100 , zorder=10 , cmap=cm_dark, marker='*' ) plt.scatter(x[0 ], x[1 ], c=y.ravel(), edgecolors='k' , s=20 , cmap=cm_dark) plt.xlabel(iris_feature[0 ], fontsize=13 ) plt.ylabel(iris_feature[1 ], fontsize=13 ) plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max) plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' , color='#606060' ) plt.title('鸢尾花数据的决策树分类' , fontsize=15 ) plt.show() y_test = y_test.reshape(-1 ) print (y_test_hat)print (y_test)result = (y_test_hat == y_test) acc = np.mean(result) print ('准确度: %.2f%%' % (100 * acc))depth = np.arange(1 , 15 ) err_train_list = [] err_test_list = [] clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy' ) for d in depth: clf.set_params(max_depth=d) clf.fit(x_train, y_train) y_train_pred = clf.predict(x_train) err_train = 1 - accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred) err_train_list.append(err_train) y_test_pred = clf.predict(x_test) err_test = 1 - accuracy_score(y_test, y_test_pred) err_test_list.append(err_test) print (d, ' 测试集错误率: %.2f%%' % (100 * err_test)) plt.figure(facecolor='w' ) plt.plot(depth, err_test_list, 'ro-' , markeredgecolor='k' , lw=2 , label='测试集错误率' ) plt.plot(depth, err_train_list, 'go-' , markeredgecolor='k' , lw=2 , label='训练集错误率' ) plt.xlabel('决策树深度' , fontsize=13 ) plt.ylabel('错误率' , fontsize=13 ) plt.legend(loc='lower left' , fontsize=13 ) plt.title('决策树深度与过拟合' , fontsize=15 ) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' , color='#606060' ) plt.show()
训练集正确率: 0.9523809523809523
测试集正确率: 0.6222222222222222
(2500, 2)
x_show =
[[4.3 2. ]
[4.37346939 2. ]
[4.44693878 2. ]
...
[7.75306122 4.4 ]
[7.82653061 4.4 ]
[7.9 4.4 ]]
(2500,)
[0 0 0 ... 2 2 2]
[[0 0 0 ... 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 ... 1 1 1]
[0 0 0 ... 1 1 1]
...
[0 0 0 ... 2 2 2]
[0 0 0 ... 2 2 2]
[0 0 0 ... 2 2 2]]
[0 1 2 0 2 2 1 0 0 2 2 0 1 2 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 1 0 0 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 0 1
0 2 1 2 0 1 1 1]
[0 1 1 0 2 1 2 0 0 2 1 0 2 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 2 1 0 0 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 0 1
0 1 2 2 0 2 2 1]
准确度: 62.22%
1 测试集错误率: 44.44%
2 测试集错误率: 40.00%
3 测试集错误率: 20.00%
4 测试集错误率: 24.44%
5 测试集错误率: 24.44%
6 测试集错误率: 28.89%
7 测试集错误率: 37.78%
8 测试集错误率: 40.00%
9 测试集错误率: 37.78%
10 测试集错误率: 40.00%
11 测试集错误率: 37.78%
12 测试集错误率: 37.78%
13 测试集错误率: 40.00%
14 测试集错误率: 37.78%
随机森林 import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib as mplimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scorefrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitmpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif' ] = ['SimHei' ] mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus' ] = False iris_feature = u'花萼长度' , u'花萼宽度' , u'花瓣长度' , u'花瓣宽度' path = './_data_set/iris_classification/iris.data' data = pd.read_csv(path, header=None ) x_prime = data[list (range (4 ))] y = pd.Categorical(data[4 ]).codes x_prime_train, x_prime_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_prime, y, train_size=0.7 , random_state=0 ) feature_pairs = [[0 , 1 ], [0 , 2 ], [0 , 3 ], [1 , 2 ], [1 , 3 ], [2 , 3 ]] plt.figure(figsize=(8 , 6 ), facecolor='#FFFFFF' ) for i, pair in enumerate (feature_pairs): x_train = x_prime_train[pair] x_test = x_prime_test[pair] model = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy' , min_samples_leaf=3 ) model.fit(x_train, y_train) N, M = 500 , 500 x1_min, x2_min = x_train.min () x1_max, x2_max = x_train.max () t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, N) t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, M) x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2) x_show = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1 ) y_train_pred = model.predict(x_train) acc_train = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred) y_test_pred = model.predict(x_test) acc_test = accuracy_score(y_test, y_test_pred) print ('特征:' , iris_feature[pair[0 ]], ' + ' , iris_feature[pair[1 ]]) print ('\t训练集准确率: %.4f%%' % (100 * acc_train)) print ('\t测试集准确率: %.4f%%\n' % (100 * acc_test)) cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0' , '#FFA0A0' , '#A0A0FF' ]) cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g' , 'r' , 'b' ]) y_hat = model.predict(x_show) y_hat = y_hat.reshape(x1.shape) plt.subplot(2 , 3 , i + 1 ) plt.contour(x1, x2, y_hat, colors='k' , levels=[0 , 1 ], antialiased=True , linewidths=1 ) plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_hat, cmap=cm_light, shading='auto' ) plt.scatter(x_train[pair[0 ]], x_train[pair[1 ]], c=y_train, s=20 , edgecolors='k' , cmap=cm_dark, label=u'训练集' ) plt.scatter(x_test[pair[0 ]], x_test[pair[1 ]], c=y_test, s=80 , marker='*' , edgecolors='k' , cmap=cm_dark, label=u'测试集' ) plt.xlabel(iris_feature[pair[0 ]], fontsize=12 ) plt.ylabel(iris_feature[pair[1 ]], fontsize=12 ) plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max) plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' , color='#606060' ) plt.suptitle(u'决策树对鸢尾花数据两特征组合的分类结果' , fontsize=15 ) plt.tight_layout(1 , rect=(0 , 0 , 1 , 0.94 )) plt.show()
特征: 花萼长度 + 花萼宽度
训练集准确率: 85.7143%
测试集准确率: 71.1111%
特征: 花萼长度 + 花瓣长度
训练集准确率: 96.1905%
测试集准确率: 91.1111%
特征: 花萼长度 + 花瓣宽度
训练集准确率: 96.1905%
测试集准确率: 86.6667%
特征: 花萼宽度 + 花瓣长度
训练集准确率: 97.1429%
测试集准确率: 95.5556%
特征: 花萼宽度 + 花瓣宽度
训练集准确率: 96.1905%
测试集准确率: 84.4444%
特征: 花瓣长度 + 花瓣宽度
训练集准确率: 98.0952%
测试集准确率: 97.7778%
C:\Users\utsuk\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_25000\2108356862.py:83: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: Passing the pad parameter of tight_layout() positionally is deprecated since Matplotlib 3.3; the parameter will become keyword-only two minor releases later.
plt.tight_layout(1, rect=(0, 0, 1, 0.94)) # (left, bottom, right, top)
决策树-随机森林回归 import numpy as npimport matplotlib as mplimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressorN = 100 x = np.random.rand(N) * 6 - 3 x.sort() y = np.sin(x) + np.random.randn(N) * 0.05 x = x.reshape(-1 , 1 ) print (x)print (y)model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=20 , criterion='mse' , max_depth=10 ) model.fit(x, y) x_test = np.linspace(-3 , 3 , 50 ).reshape(-1 , 1 ) y_hat = model.predict(x_test) mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif' ] = ['SimHei' ] mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus' ] = False plt.figure(facecolor='w' ) plt.plot(x, y, 'r*' , markersize=10 , markeredgecolor='k' , label='实际值' ) plt.plot(x_test, y_hat, 'g-' , linewidth=2 , label='预测值' ) plt.legend(loc='upper left' , fontsize=12 ) plt.xlabel('X' ) plt.ylabel('Y' ) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' , color='#606060' ) plt.title('决策树-随机森林回归' , fontsize=15 ) plt.tight_layout(2 ) plt.show() depth = [2 , 4 , 6 , 8 , 10 ] clr = 'rgbmy' model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=20 , criterion='mse' ) plt.figure(facecolor='w' ) plt.plot(x, y, 'ro' , ms=5 , mec='k' , label='实际值' ) x_test = np.linspace(-3 , 3 , 50 ).reshape(-1 , 1 ) for d, c in zip (depth, clr): model.set_params(max_depth=d) model.fit(x, y) y_hat = model.predict(x_test) plt.plot(x_test, y_hat, '-' , color=c, linewidth=2 , markeredgecolor='k' , label='Depth=%d' % d) plt.legend(loc='upper left' , fontsize=12 ) plt.xlabel('X' ) plt.ylabel('Y' ) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' , color='#606060' ) plt.title('决策树-随机森林回归' , fontsize=15 ) plt.tight_layout(2 ) plt.show()
[[-2.95013857]
[-2.91406777]
[-2.90709403]
[-2.90375999]
[-2.87745415]
[-2.86685497]
[-2.84070033]
[-2.81375697]
[-2.77943784]
[-2.77745775]
[-2.66347611]
[-2.65986762]
[-2.64217075]
[-2.63778267]
[-2.63639243]
[-2.60165162]
[-2.48896096]
[-2.43041085]
[-2.39941506]
[-2.38779079]
[-2.37856289]
[-2.32809632]
[-2.29426051]
[-2.25524085]
[-2.23914776]
[-2.16578847]
[-2.0055294 ]
[-1.9885004 ]
[-1.73199798]
[-1.61893958]
[-1.58908223]
[-1.54966302]
[-1.49074428]
[-1.46530843]
[-1.40362808]
[-1.3935955 ]
[-1.3928819 ]
[-1.37684247]
[-1.3377295 ]
[-1.33035029]
[-1.24577529]
[-1.15561278]
[-1.12976361]
[-0.92771942]
[-0.91536325]
[-0.83851709]
[-0.54828961]
[-0.54587447]
[-0.54456521]
[-0.51610774]
[-0.38078143]
[-0.27298529]
[-0.20898971]
[-0.20866835]
[ 0.01703485]
[ 0.03203468]
[ 0.06107388]
[ 0.07358949]
[ 0.07361575]
[ 0.10676155]
[ 0.15818226]
[ 0.20123638]
[ 0.3410772 ]
[ 0.45680655]
[ 0.52384169]
[ 0.65741898]
[ 0.68306354]
[ 0.82845395]
[ 0.83952908]
[ 0.99278446]
[ 1.04865533]
[ 1.16809926]
[ 1.21294563]
[ 1.44659934]
[ 1.47606149]
[ 1.48031876]
[ 1.54476213]
[ 1.54542061]
[ 1.60452852]
[ 1.85706958]
[ 1.9814776 ]
[ 2.07801869]
[ 2.08420295]
[ 2.08974078]
[ 2.09458999]
[ 2.21547939]
[ 2.2354401 ]
[ 2.2824592 ]
[ 2.39313024]
[ 2.4822308 ]
[ 2.5275393 ]
[ 2.56392915]
[ 2.63696096]
[ 2.65318554]
[ 2.66286196]
[ 2.67531127]
[ 2.69337798]
[ 2.78329004]
[ 2.83409465]
[ 2.94897411]]
[-0.16517944 -0.2651016 -0.26383212 -0.2408083 -0.21137157 -0.30729908
-0.24489794 -0.42738593 -0.39536257 -0.34762803 -0.55252409 -0.40629331
-0.47658554 -0.47459876 -0.50897455 -0.58933727 -0.57144697 -0.61564276
-0.76543047 -0.64009055 -0.79612233 -0.77625958 -0.82824783 -0.74228023
-0.6882561 -0.85479709 -0.9210133 -0.88824326 -0.94228155 -1.04205908
-1.01456756 -1.0150173 -1.01319155 -0.93942161 -1.0101109 -1.00949492
-1.00669835 -1.02762794 -0.90526463 -1.04873446 -0.98356087 -0.96345712
-0.90790305 -0.78617335 -0.8215092 -0.7756252 -0.62805774 -0.61416394
-0.55438357 -0.54877048 -0.24409899 -0.24654351 -0.22139215 -0.31816396
-0.00948097 0.03731195 0.07871564 0.06089414 0.091661 0.10130855
0.05916354 0.284293 0.32301758 0.47390064 0.43774825 0.59439442
0.62285701 0.78479681 0.7888438 0.91498224 0.91654605 0.84583033
0.90598404 0.99494553 1.05048367 0.97256267 1.04768316 1.09246729
0.92367061 0.97097779 0.98148804 0.86766162 0.87249721 0.81545132
0.80772307 0.75639662 0.73792794 0.75909448 0.71239606 0.63892773
0.6373865 0.53978973 0.47836416 0.47544309 0.4156747 0.46233128
0.43384357 0.32001956 0.2980857 0.16211947]
C:\Users\utsuk\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_25000\2984870596.py:33: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: Passing the pad parameter of tight_layout() positionally is deprecated since Matplotlib 3.3; the parameter will become keyword-only two minor releases later.
plt.tight_layout(2)
C:\Users\utsuk\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_25000\2984870596.py:60: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: Passing the pad parameter of tight_layout() positionally is deprecated since Matplotlib 3.3; the parameter will become keyword-only two minor releases later.
plt.tight_layout(2)
分类问题 逻辑回归 二分类 import numpy as npimport sklearn.linear_model as lmimport matplotlib.pyplot as mpx = np.array([[3 , 1 ], [2 , 5 ], [1 , 8 ], [6 , 4 ],\ [5 , 2 ], [3 , 5 ], [4 , 7 ], [4 , -1 ]]) y = np.array([0 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 0 ]) model = lm.LogisticRegression() model.fit(x, y) test_x = np.array([[3 , 9 ], [6 , 1 ]]) test_y = model.predict(test_x) print (test_y)left = x[:, 0 ].min () - 1 right = x[:, 0 ].max () + 1 buttom = x[:, 1 ].min () - 1 top = x[:, 1 ].max () + 1 grid_x, grid_y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(left, right, 0.01 ), np.arange(buttom, top, 0.01 )) print ("grid_x.shape:" , grid_x.shape)print ("grid_y.shape:" , grid_y.shape)mesh_x = np.column_stack((grid_x.ravel(), grid_y.ravel())) print ("mesh_x.shape:" , mesh_x.shape)mesh_z = model.predict(mesh_x) mesh_z = mesh_z.reshape(grid_x.shape) mp.figure('Logistic Regression' , facecolor='lightgray' ) mp.title('Logistic Regression' , fontsize=20 ) mp.xlabel('x' , fontsize=14 ) mp.ylabel('y' , fontsize=14 ) mp.tick_params(labelsize=10 ) mp.pcolormesh(grid_x, grid_y, mesh_z, cmap='gray' , shading='auto' ) mp.scatter( x[:, 0 ], x[:, 1 ], c=y, cmap='brg' , s=80 ) mp.scatter(test_x[:, 0 ], test_x[:, 1 ], c="red" , marker='s' , s=80 ) mp.show()
[1 0]
grid_x.shape: (1100, 700)
grid_y.shape: (1100, 700)
mesh_x.shape: (770000, 2)
多分类 import numpy as npimport sklearn.linear_model as lmimport matplotlib.pyplot as mpx = np.array([[4 , 7 ], [3.5 , 8 ], [3.1 , 6.2 ], [0.5 , 1 ], [1 , 2 ], [1.2 , 1.9 ], [6 , 2 ], [5.7 , 1.5 ], [5.4 , 2.2 ]]) y = np.array([0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 2 , 2 , 2 ]) model = lm.LogisticRegression(C=200 ) model.fit(x, y) left = x[:, 0 ].min () - 1 right = x[:, 0 ].max () + 1 h = 0.005 buttom = x[:, 1 ].min () - 1 top = x[:, 1 ].max () + 1 v = 0.005 grid_x, grid_y = np.meshgrid(np.arange(left, right, h), np.arange(buttom, top, v)) mesh_x = np.column_stack((grid_x.ravel(), grid_y.ravel())) mesh_z = model.predict(mesh_x) mesh_z = mesh_z.reshape(grid_x.shape) mp.figure('Logistic Classification' , facecolor='lightgray' ) mp.title('Logistic Classification' , fontsize=20 ) mp.xlabel('x' , fontsize=14 ) mp.ylabel('y' , fontsize=14 ) mp.tick_params(labelsize=10 ) mp.pcolormesh(grid_x, grid_y, mesh_z, cmap='gray' , shading='auto' ) mp.scatter(x[:, 0 ], x[:, 1 ], c=y, cmap='brg' , s=80 ) mp.show()
import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npfrom datetime import datetimefrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionfrom sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_errorfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures, LabelEncoderfrom sklearn.pipeline import make_pipelineimport seaborn as snspumpkins = pd.read_csv('./_data_set/US-pumpkins.csv' ) new_pumpkins = pumpkins.drop([ c for c in pumpkins.columns if c not in ['Color' , 'Origin' , 'Item Size' , 'Variety' , 'City Name' , 'Package' ] ], axis=1 ) new_pumpkins.dropna(inplace=True ) new_pumpkins = new_pumpkins.apply(LabelEncoder().fit_transform) sns.PairGrid(new_pumpkins).map (sns.scatterplot) sns.catplot(x="Color" , y="Item Size" , kind="violin" , data=new_pumpkins)
<seaborn.axisgrid.FacetGrid at 0x19b7ed39fd0>
支持向量机-SVM 核函数 线性
径向基-高斯
import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib as mplimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn import svmfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scorefrom sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCVfrom time import timeiris_feature = '花萼长度' , '花萼宽度' , '花瓣长度' , '花瓣宽度' path = './_data_set/iris_classification/iris.data' data = pd.read_csv(path, header=None ) x, y = data[[0 , 1 ]], pd.Categorical(data[4 ]).codes x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=1 , test_size=0.4 ) svm_clf = svm.SVC(C=3 , kernel='linear' ) print ('GridSearchCV begin...' )t = time() clf = svm_clf clf.fit(x_train, y_train.ravel()) t_end = time() print ('耗时:%d秒' % (t_end - t))print (clf.score(x_train, y_train)) print ('训练集准确率:' , accuracy_score(y_train, clf.predict(x_train)))print (clf.score(x_test, y_test))print ('测试集准确率:' , accuracy_score(y_test, clf.predict(x_test)))print (x_train[:5 ])print ('decision_function:\n' , clf.decision_function(x_train))print ('\npredict:\n' , clf.predict(x_train))x1_min, x2_min = x.min () x1_max, x2_max = x.max () x1, x2 = np.mgrid[x1_min:x1_max:300j , x2_min:x2_max:300j ] grid_test = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1 ) grid_hat = clf.predict(grid_test) grid_hat = grid_hat.reshape(x1.shape) mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif' ] = ['SimHei' ] mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus' ] = False cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['#A0FFA0' , '#FFA0A0' , '#A0A0FF' ]) cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g' , 'r' , 'b' ]) plt.figure(facecolor='w' ) plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, grid_hat, cmap=cm_light, shading='auto' ) plt.scatter(x[0 ], x[1 ], c=y, edgecolors='k' , s=50 , cmap=cm_dark) plt.scatter(x_test[0 ], x_test[1 ], s=120 , facecolors='none' , zorder=10 ) plt.xlabel(iris_feature[0 ], fontsize=13 ) plt.ylabel(iris_feature[1 ], fontsize=13 ) plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max) plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max) plt.title('鸢尾花SVM二特征分类' , fontsize=16 ) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' ) plt.tight_layout(pad=1.5 ) plt.show()
GridSearchCV begin...
耗时:0秒
0.7888888888888889
训练集准确率: 0.7888888888888889
0.7833333333333333
测试集准确率: 0.7833333333333333
0 1
11 4.8 3.4
113 5.7 2.5
123 6.3 2.7
12 4.8 3.0
2 4.7 3.2
decision_function:
[[ 2.27077043 0.77466667 -0.23050192]
[-0.26084184 2.25751125 1.0560141 ]
[-0.28293421 2.25843306 1.22796515]
[ 2.24308998 0.92588576 -0.2355186 ]
[ 2.26643883 0.80879936 -0.24170145]
[-0.28069428 1.23581332 2.24817619]
[ 2.28018898 0.76457517 -0.24714914]
[-0.25832462 1.21350955 2.20811726]
[-0.27289547 1.20094518 2.249947 ]
[-0.28479994 1.2318958 2.26058535]
[-0.23449614 2.22389578 1.08207816]
[-0.27824598 1.19362022 2.2618816 ]
[-0.24940836 1.20624284 2.19142888]
[ 2.2732283 -0.2577432 0.82271427]
[-0.2872948 2.27977562 1.1680301 ]
[-0.28016055 1.24346593 2.23969255]
[-0.28069428 1.23581332 2.24817619]
[-0.17539161 2.25364746 0.77515212]
[-0.25325305 1.14281388 2.23566431]
[-0.2421088 2.25159667 0.90072452]
[ 2.24374936 -0.23761503 0.93581753]
[ 2.24150985 0.87804111 -0.2241573 ]
[ 2.28041834 -0.27382086 0.86293615]
[-0.27824598 1.19362022 2.2618816 ]
[ 2.27361996 0.84008337 -0.26180365]
[-0.26919985 2.24943754 1.18347413]
[-0.28629221 2.26101768 1.23745359]
[-0.23808639 1.19803786 2.16960812]
[ 2.24670891 -0.21840299 0.83780678]
[ 2.23817757 0.82105098 -0.19112107]
[-0.2549617 2.24213564 1.1247623 ]
[ 2.24150985 0.87804111 -0.2241573 ]
[-0.30409023 1.27536123 2.28319903]
[-0.27073104 1.23503534 2.2197061 ]
[-0.30441277 1.26883084 2.28803158]
[-0.28752494 1.24411663 2.25991942]
[-0.29292012 2.28000741 1.22212062]
[-0.23176304 1.04104242 2.22722296]
[-0.28694643 1.15125962 2.28088265]
[-0.19956441 2.19653578 1.01742803]
[ 2.26878977 -0.27918692 1.16597018]
[-0.2549617 2.24213564 1.1247623 ]
[ 2.18519501 1.23494087 -0.26146238]
[-0.2512831 2.2597216 0.89408741]
[-0.29066599 1.240849 2.26933123]
[ 2.25729439 -0.2129225 0.79411601]
[-0.29441953 1.26382422 2.26345809]
[ 2.26377705 -0.22976306 0.79617407]
[ 2.27077043 0.77466667 -0.23050192]
[-0.2445374 1.07681969 2.23683943]
[-0.21840757 2.21786592 1.00447438]
[-0.28524498 1.22203776 2.26581127]
[ 2.24947915 0.81045802 -0.20787766]
[ 2.2684482 -0.24915018 0.81973595]
[-0.20907334 1.12013512 2.17603067]
[ 2.26728139 0.82893904 -0.24984081]
[-0.2549617 2.24213564 1.1247623 ]
[ 2.25207771 0.85867453 -0.23431088]
[-0.28069428 1.23581332 2.24817619]
[ 1.05055292 2.22662497 -0.23240122]
[ 2.2722284 0.7997718 -0.24896247]
[-0.26723747 1.19201787 2.24286157]
[ 2.27827649 0.82682975 -0.26630655]
[-0.17333043 2.16553945 1.02939988]
[ 2.26890439 0.89311197 -0.26243597]
[-0.2512831 2.2597216 0.89408741]
[-0.23341849 2.27309387 0.7709214 ]
[ 2.25617562 -0.22437834 0.81410784]
[ 2.22986475 0.96247553 -0.22562355]
[ 0.93771503 2.24006469 -0.23365567]
[ 2.28631446 -0.25590025 0.75474384]
[-0.23808639 1.19803786 2.16960812]
[-0.2646401 1.23019768 2.20613126]
[ 2.25729439 -0.2129225 0.79411601]
[-0.28479994 1.2318958 2.26058535]
[-0.22087216 2.20491832 1.08971052]
[-0.29260626 2.28238001 1.20719635]
[-0.29101034 1.23272406 2.27341138]
[-0.2549617 2.24213564 1.1247623 ]
[ 2.19974418 -0.17699012 0.91119813]
[ 2.21209755 1.01040036 -0.21350121]
[-0.27849238 2.26059076 1.19977637]
[-0.26997469 2.24280567 1.20408124]
[-0.29874557 1.25977449 2.27874043]
[-0.25377271 2.24886239 1.06528288]
[-0.27961589 2.2500049 1.22933155]
[-0.27219081 1.21466357 2.24182934]
[-0.2884762 2.2710352 1.22512174]
[-0.28479994 1.2318958 2.26058535]
[ 2.24150985 0.87804111 -0.2241573 ]]
predict:
[0 1 1 0 0 2 0 2 2 2 1 2 2 0 1 2 2 1 2 1 0 0 0 2 0 1 1 2 0 0 1 0 2 2 2 2 1
2 2 1 0 1 0 1 2 0 2 0 0 2 1 2 0 0 2 0 1 0 2 1 0 2 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 2 2 0
2 1 1 2 1 0 0 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 0]
import numpy as npfrom sklearn import svmfrom scipy import statsfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_scoreimport matplotlib as mplimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef extend (a, b, r=0.01 ): return a * (1 + r) - b * r, -a * r + b * (1 + r) np.random.seed(0 ) N = 200 x = np.empty((4 * N, 2 )) means = [(-1 , 1 ), (1 , 1 ), (1 , -1 ), (-1 , -1 )] sigmas = [ np.eye(2 ), 2 * np.eye(2 ), np.diag((1 , 2 )), np.array(((3 , 2 ), (2 , 3 ))) ] for i in range (4 ): mn = stats.multivariate_normal(means[i], sigmas[i] * 0.07 ) x[i * N:(i + 1 ) * N, :] = mn.rvs(N) a = np.array((0 , 1 , 2 , 3 )).reshape((-1 , 1 )) y = np.tile(a, N).flatten() clf = svm.SVC(C=1 , kernel='rbf' , gamma=1 , decision_function_shape='ovo' ) clf.fit(x, y) y_hat = clf.predict(x) acc = accuracy_score(y, y_hat) np.set_printoptions(suppress=True ) print ('预测正确的样本个数:%d,正确率:%.2f%%' % (round (acc * 4 * N), 100 * acc))print (clf.decision_function(x))print (y_hat)x1_min, x2_min = np.min (x, axis=0 ) x1_max, x2_max = np.max (x, axis=0 ) x1_min, x1_max = extend(x1_min, x1_max) x2_min, x2_max = extend(x2_min, x2_max) x1, x2 = np.mgrid[x1_min:x1_max:500j , x2_min:x2_max:500j ] x_test = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1 ) y_test = clf.predict(x_test) y_test = y_test.reshape(x1.shape) cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap( ['#FF8080' , '#80FF80' , '#8080FF' , '#F0F080' ]) cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['r' , 'g' , 'b' , 'y' ]) mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif' ] = ['SimHei' ] mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus' ] = False plt.figure(facecolor='w' ) plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_test, cmap=cm_light, shading='auto' ) plt.contour(x1, x2, y_test, levels=(0 , 1 , 2 ), colors='k' , linestyles='--' ) plt.scatter(x[:, 0 ], x[:, 1 ], s=20 , c=y, cmap=cm_dark, edgecolors='k' , alpha=0.7 ) plt.xlabel('$X_1$' , fontsize=11 ) plt.ylabel('$X_2$' , fontsize=11 ) plt.xlim((x1_min, x1_max)) plt.ylim((x2_min, x2_max)) plt.grid(b=True ) plt.tight_layout(pad=2.5 ) plt.title('SVM多分类方法:One/One or One/Other' , fontsize=14 ) plt.show()
预测正确的样本个数:793,正确率:99.12%
[[ 1.30403817 1.18371967 1.61069453 0.53379555 0.10282667 -0.6639782 ]
[ 1.20484592 1.00041165 1.13023042 0.32840742 0.16888308 -0.33559223]
[ 1.28448754 1.15305262 1.24310512 0.59725054 -0.31474389 -0.97622623]
...
[-0.23584035 -0.08224918 -1.09483656 0.1554822 -1.12200744 -1.12840424]
[ 0.2447751 0.34444513 -1.55255237 0.17064062 -1.24348982 -1.41973039]
[-0.03070327 -0.15566364 -1.9254549 -0.09600454 -1.23897289 -1.44257329]]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3]
朴素贝叶斯 class NBClassify (object ): def __init__ (self, fillNa=1 ): self .fillNa = 1 pass def train (self, trainSet ): dictTag = {} for subTuple in trainSet: dictTag[str ( subTuple[1 ])] = 1 if str (subTuple[1 ]) not in dictTag.keys( ) else dictTag[str (subTuple[1 ])] + 1 tagProbablity = {} totalFreq = sum ([value for value in dictTag.values()]) for key, value in dictTag.items(): tagProbablity[key] = value / totalFreq self .tagProbablity = tagProbablity dictFeaturesBase = {} for subTuple in trainSet: for key, value in subTuple[0 ].items(): if key not in dictFeaturesBase.keys(): dictFeaturesBase[key] = {value: 1 } else : if value not in dictFeaturesBase[key].keys(): dictFeaturesBase[key][value] = 1 else : dictFeaturesBase[key][value] += 1 dictFeatures = {}.fromkeys([key for key in dictTag]) for key in dictFeatures.keys(): dictFeatures[key] = {}.fromkeys([key for key in dictFeaturesBase]) for key, value in dictFeatures.items(): for subkey in value.keys(): value[subkey] = {}.fromkeys( [x for x in dictFeaturesBase[subkey].keys()]) for subTuple in trainSet: for key, value in subTuple[0 ].items(): dictFeatures[subTuple[1 ]][key][value] = 1 if dictFeatures[ subTuple[1 ]][key][value] == None else dictFeatures[ subTuple[1 ]][key][value] + 1 for tag, featuresDict in dictFeatures.items(): for featureName, fetureValueDict in featuresDict.items(): for featureKey, featureValues in fetureValueDict.items(): if featureValues == None : fetureValueDict[featureKey] = 1 for tag, featuresDict in dictFeatures.items(): for featureName, fetureValueDict in featuresDict.items(): totalCount = sum ( [x for x in fetureValueDict.values() if x != None ]) for featureKey, featureValues in fetureValueDict.items(): fetureValueDict[ featureKey] = featureValues / totalCount if featureValues != None else None self .featuresProbablity = dictFeatures def classify (self, featureDict ): resultDict = {} for key, value in self .tagProbablity.items(): iNumList = [] for f, v in featureDict.items(): if self .featuresProbablity[key][f][v]: iNumList.append(self .featuresProbablity[key][f][v]) conditionPr = 1 for iNum in iNumList: conditionPr *= iNum resultDict[key] = value * conditionPr resultList = sorted (resultDict.items(), key=lambda x: x[1 ], reverse=True ) return resultList[0 ][0 ] if __name__ == '__main__' : trainSet = [ ({ "症状" : "打喷嚏" , "职业" : "护士" }, "感冒 " ), ({ "症状" : "打喷嚏" , "职业" : "农夫" }, "过敏 " ), ({ "症状" : "头痛" , "职业" : "建筑工人" }, "脑震荡" ), ({ "症状" : "头痛" , "职业" : "建筑工人" }, "感冒 " ), ({ "症状" : "打喷嚏" , "职业" : "教师" }, "感冒 " ), ({ "症状" : "头痛" , "职业" : "教师" }, "脑震荡" ), ] monitor = NBClassify() monitor.train(trainSet) result = monitor.classify({"症状" : "打喷嚏" , "职业" : "建筑工人" }) print (result)
感冒
多元问题-菜肴分类 数据加载与清洗 import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport matplotlib as mplimport numpy as npfrom imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTEdf = pd.read_csv('./_data_set/cuisines_classification/cuisines.csv' ) df.head()
Unnamed: 0 cuisine almond angelica anise anise_seed apple apple_brandy apricot armagnac ... whiskey white_bread white_wine whole_grain_wheat_flour wine wood yam yeast yogurt zucchini 0 65 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 66 indian 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 67 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 68 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 69 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
5 rows × 385 columns
def create_ingredient_df (df ): ingredient_df = df.T.drop(['cuisine' , 'Unnamed: 0' ]).sum (axis=1 ).to_frame('value' ) ingredient_df = ingredient_df[(ingredient_df.T != 0 ).any ()] ingredient_df = ingredient_df.sort_values(by='value' , ascending=False , inplace=False ) return ingredient_df for i in ["thai" , "japanese" , "chinese" , "indian" , "korean" ]: ingredient_df = create_ingredient_df(df[(df.cuisine == i)]) ingredient_df.head(10 ).plot.barh().set_title(i) feature_df = df.drop(['cuisine' , 'Unnamed: 0' , 'rice' , 'garlic' , 'ginger' ], axis=1 ) labels_df = df.cuisine
transformed_feature_df, transformed_label_df = SMOTE().fit_resample( feature_df, labels_df) print ( f'===================== old label count: ===================== \n{labels_df.value_counts()} \ \n===================== new label count: ===================== \n{transformed_label_df.value_counts()} ' ) transformed_df = pd.concat([transformed_label_df, transformed_feature_df], axis=1 , join='outer' ) transformed_df.info() transformed_df.to_csv("./_data_set/cuisines_classification/cleaned_cuisines.csv" )
===================== old label count: =====================
korean 799
indian 598
chinese 442
japanese 320
thai 289
Name: cuisine, dtype: int64
===================== new label count: =====================
indian 799
thai 799
chinese 799
japanese 799
korean 799
Name: cuisine, dtype: int64
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 3995 entries, 0 to 3994
Columns: 381 entries, cuisine to zucchini
dtypes: int64(380), object(1)
memory usage: 11.6+ MB
分类-1 import pandas as pdfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_scorefrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report, precision_recall_curvefrom sklearn.svm import SVCimport numpy as npcuisines_df = pd.read_csv( "./_data_set/cuisines_classification/cleaned_cuisines.csv" ) cuisines_df.head()
Unnamed: 0 cuisine almond angelica anise anise_seed apple apple_brandy apricot armagnac ... whiskey white_bread white_wine whole_grain_wheat_flour wine wood yam yeast yogurt zucchini 0 0 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 indian 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 indian 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
5 rows × 382 columns
cuisines_label_df = cuisines_df['cuisine' ] cuisines_feature_df = cuisines_df.drop(['Unnamed: 0' , 'cuisine' ], axis=1 ) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(cuisines_feature_df, cuisines_label_df, test_size=0.3 ) """ 1137 korean 428 thai 191 indian 1336 korean 3947 thai ... 3335 japanese 3539 thai 436 thai 1875 indian 3079 japanese Name: cuisine, Length: 2796, dtype: object ['korean' 'thai' 'indian' ... 'thai' 'indian' 'japanese'] """ model = LogisticRegression(multi_class='ovr' , solver='liblinear' ).fit(X_train, np.ravel(y_train)) accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test) print (f"Accuracy is {accuracy} " )
Accuracy is 0.7906588824020017
line_num = 50 print (f'ingredients: {X_test.iloc[line_num][X_test.iloc[line_num]!=0 ].keys()} ' )print (f'cuisine: {y_test.iloc[line_num]} ' )test = X_test.iloc[line_num].values.reshape(-1 , 1 ).T proba = model.predict_proba(test) classes = model.classes_ resultdf = pd.DataFrame(data=proba, columns=classes) topPrediction = resultdf.T.sort_values(by=[0 ], ascending=[False ]) topPrediction.head()
ingredients: Index(['butter', 'cayenne', 'cheese', 'cinnamon', 'coriander', 'onion',
'tomato', 'turmeric'],
dtype='object')
cuisine: indian
D:\Scoop\apps\anaconda3\current\lib\site-packages\sklearn\base.py:450: UserWarning: X does not have valid feature names, but LogisticRegression was fitted with feature names
warnings.warn(
0 indian 0.962110 thai 0.021403 korean 0.011124 japanese 0.003710 chinese 0.001653
y_pred = model.predict(X_test) print (classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
precision recall f1-score support
chinese 0.76 0.68 0.72 242
indian 0.91 0.93 0.92 239
japanese 0.72 0.76 0.74 222
korean 0.84 0.80 0.82 264
thai 0.77 0.84 0.80 232
accuracy 0.80 1199
macro avg 0.80 0.80 0.80 1199
weighted avg 0.80 0.80 0.80 1199
分类-2 from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifierfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.svm import SVCfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifierfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_scorefrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report, precision_recall_curveimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdcuisines_df = pd.read_csv( "./_data_set/cuisines_classification/cleaned_cuisines.csv" ) cuisines_label_df = cuisines_df['cuisine' ] cuisines_feature_df = cuisines_df.drop(['Unnamed: 0' , 'cuisine' ], axis=1 ) X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(cuisines_feature_df, cuisines_label_df, test_size=0.3 )
C = 10 classifiers = { 'Linear SVC' : SVC(kernel='linear' , C=C, probability=True , random_state=0 ), 'KNN classifier' : KNeighborsClassifier(C), 'SVC' : SVC(), 'RFST' : RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100 ), 'ADA' : AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=100 ) } for index, (name, classifier) in enumerate (classifiers.items()): classifier.fit(X_train, np.ravel(y_train)) y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test) accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) print ("Accuracy (train) for %s: %0.1f%%" % (name, accuracy * 100 )) print (classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
Accuracy (train) for Linear SVC: 80.2%
precision recall f1-score support
chinese 0.73 0.76 0.74 250
indian 0.86 0.89 0.88 235
japanese 0.78 0.78 0.78 245
korean 0.88 0.74 0.80 227
thai 0.78 0.84 0.81 242
accuracy 0.80 1199
macro avg 0.81 0.80 0.80 1199
weighted avg 0.81 0.80 0.80 1199
Accuracy (train) for KNN classifier: 73.6%
precision recall f1-score support
chinese 0.71 0.73 0.72 250
indian 0.80 0.86 0.83 235
japanese 0.67 0.80 0.73 245
korean 0.91 0.51 0.65 227
thai 0.69 0.77 0.73 242
accuracy 0.74 1199
macro avg 0.76 0.73 0.73 1199
weighted avg 0.75 0.74 0.73 1199
Accuracy (train) for SVC: 82.8%
precision recall f1-score support
chinese 0.77 0.81 0.79 250
indian 0.88 0.93 0.90 235
japanese 0.82 0.76 0.79 245
korean 0.90 0.77 0.83 227
thai 0.79 0.88 0.83 242
accuracy 0.83 1199
macro avg 0.83 0.83 0.83 1199
weighted avg 0.83 0.83 0.83 1199
Accuracy (train) for RFST: 84.5%
precision recall f1-score support
chinese 0.82 0.81 0.82 250
indian 0.85 0.93 0.89 235
japanese 0.86 0.81 0.83 245
korean 0.90 0.83 0.86 227
thai 0.81 0.85 0.83 242
accuracy 0.84 1199
macro avg 0.85 0.85 0.85 1199
weighted avg 0.85 0.84 0.84 1199
Accuracy (train) for ADA: 69.3%
precision recall f1-score support
chinese 0.64 0.42 0.51 250
indian 0.81 0.85 0.83 235
japanese 0.65 0.61 0.63 245
korean 0.62 0.82 0.71 227
thai 0.73 0.79 0.76 242
accuracy 0.69 1199
macro avg 0.69 0.70 0.69 1199
weighted avg 0.69 0.69 0.68 1199
聚类问题 聚类入门-数据分布 import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pddf = pd.read_csv("./_data_set/Clustering/nigerian-songs.csv" ) df.info() df.describe()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 530 entries, 0 to 529
Data columns (total 16 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 name 530 non-null object
1 album 530 non-null object
2 artist 530 non-null object
3 artist_top_genre 530 non-null object
4 release_date 530 non-null int64
5 length 530 non-null int64
6 popularity 530 non-null int64
7 danceability 530 non-null float64
8 acousticness 530 non-null float64
9 energy 530 non-null float64
10 instrumentalness 530 non-null float64
11 liveness 530 non-null float64
12 loudness 530 non-null float64
13 speechiness 530 non-null float64
14 tempo 530 non-null float64
15 time_signature 530 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(8), int64(4), object(4)
memory usage: 66.4+ KB
release_date length popularity danceability acousticness energy instrumentalness liveness loudness speechiness tempo time_signature count 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 530.000000 mean 2015.390566 222298.169811 17.507547 0.741619 0.265412 0.760623 0.016305 0.147308 -4.953011 0.130748 116.487864 3.986792 std 3.131688 39696.822259 18.992212 0.117522 0.208342 0.148533 0.090321 0.123588 2.464186 0.092939 23.518601 0.333701 min 1998.000000 89488.000000 0.000000 0.255000 0.000665 0.111000 0.000000 0.028300 -19.362000 0.027800 61.695000 3.000000 25% 2014.000000 199305.000000 0.000000 0.681000 0.089525 0.669000 0.000000 0.075650 -6.298750 0.059100 102.961250 4.000000 50% 2016.000000 218509.000000 13.000000 0.761000 0.220500 0.784500 0.000004 0.103500 -4.558500 0.097950 112.714500 4.000000 75% 2017.000000 242098.500000 31.000000 0.829500 0.403000 0.875750 0.000234 0.164000 -3.331000 0.177000 125.039250 4.000000 max 2020.000000 511738.000000 73.000000 0.966000 0.954000 0.995000 0.910000 0.811000 0.582000 0.514000 206.007000 5.000000
import seaborn as snsdef draw (df ): top = df['artist_top_genre' ].value_counts() plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 7 )) sns.barplot(x=top[:5 ].index, y=top[:5 ].values) plt.xticks(rotation=45 ) plt.title('Top genres' , color='blue' ) draw(df) new_df = df[df['artist_top_genre' ] != 'Missing' ] draw(new_df) featured_df = new_df[((new_df['artist_top_genre' ] == 'afro dancehall' ) | (new_df['artist_top_genre' ] == 'afropop' ) | (new_df['artist_top_genre' ] == 'nigerian pop' )) & (new_df['popularity' ] > 0 )] draw(featured_df) corrmat = featured_df.corr() f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12 , 9 )) sns.heatmap(corrmat, vmax=.8 , square=True )
<AxesSubplot:>
K-Means-与衡量指标 入门-音乐分类 !pip install seaborn import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdimport seaborn as snsdf = pd.read_csv("./_data_set/Clustering/nigerian-songs.csv" ) df.head()
Looking in indexes: http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
Requirement already satisfied: seaborn in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (0.11.2)
Requirement already satisfied: scipy>=1.0 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from seaborn) (1.7.1)
Requirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.15 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from seaborn) (1.20.3)
Requirement already satisfied: pandas>=0.23 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from seaborn) (1.4.2)
Requirement already satisfied: matplotlib>=2.2 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from seaborn) (3.4.3)
Requirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2.7 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.2->seaborn) (2.8.2)
Requirement already satisfied: cycler>=0.10 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.2->seaborn) (0.11.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pyparsing>=2.2.1 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.2->seaborn) (3.0.4)
Requirement already satisfied: kiwisolver>=1.0.1 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.2->seaborn) (1.3.2)
Requirement already satisfied: pillow>=6.2.0 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from matplotlib>=2.2->seaborn) (9.0.1)
Requirement already satisfied: pytz>=2020.1 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from pandas>=0.23->seaborn) (2021.3)
Requirement already satisfied: six>=1.5 in d:\scoop\apps\anaconda3\2021.11\lib\site-packages (from python-dateutil>=2.7->matplotlib>=2.2->seaborn) (1.16.0)
name album artist artist_top_genre release_date length popularity danceability acousticness energy instrumentalness liveness loudness speechiness tempo time_signature 0 Sparky Mandy & The Jungle Cruel Santino alternative r&b 2019 144000 48 0.666 0.8510 0.420 0.534000 0.1100 -6.699 0.0829 133.015 5 1 shuga rush EVERYTHING YOU HEARD IS TRUE Odunsi (The Engine) afropop 2020 89488 30 0.710 0.0822 0.683 0.000169 0.1010 -5.640 0.3600 129.993 3 2 LITT! LITT! AYLØ indie r&b 2018 207758 40 0.836 0.2720 0.564 0.000537 0.1100 -7.127 0.0424 130.005 4 3 Confident / Feeling Cool Enjoy Your Life Lady Donli nigerian pop 2019 175135 14 0.894 0.7980 0.611 0.000187 0.0964 -4.961 0.1130 111.087 4 4 wanted you rare. Odunsi (The Engine) afropop 2018 152049 25 0.702 0.1160 0.833 0.910000 0.3480 -6.044 0.0447 105.115 4
fetured_df = df[((df['artist_top_genre' ] == 'afro dancehall' ) | (df['artist_top_genre' ] == 'afropop' ) | (df['artist_top_genre' ] == 'nigerian pop' )) & (df['popularity' ] > 0 )] top = fetured_df['artist_top_genre' ].value_counts() plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 7 )) sns.barplot(x=top.index, y=top.values) plt.xticks(rotation=45 ) plt.title('Top genres' , color='blue' ) plt.figure(figsize=(20 , 20 ), dpi=200 ) """ plt.subplot(4, 3, 1) sns.boxplot(x='popularity', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 2) sns.boxplot(x='acousticness', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 3) sns.boxplot(x='energy', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 4) sns.boxplot(x='instrumentalness', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 5) sns.boxplot(x='liveness', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 6) sns.boxplot(x='loudness', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 7) sns.boxplot(x='speechiness', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 8) sns.boxplot(x='tempo', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 9) sns.boxplot(x='time_signature', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 10) sns.boxplot(x='danceability', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 11) sns.boxplot(x='length', data=df) plt.subplot(4, 3, 12) sns.boxplot(x='release_date', data=df) """ for i, v in enumerate ([ "popularity" , "acousticness" , "energy" , "instrumentalness" , "liveness" , "loudness" , "speechiness" , "tempo" , "time_signature" , "danceability" , "length" , "release_date" ]): plt.subplot(4 , 3 , i + 1 ) sns.boxplot(x=v, data=df)
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoderfrom sklearn.cluster import KMeansfrom sklearn import metricsle = LabelEncoder() X = df.loc[:, ('artist_top_genre' , 'popularity' , 'danceability' , 'acousticness' , 'loudness' , 'energy' )] X['artist_top_genre' ] = le.fit_transform(X['artist_top_genre' ]) y = le.transform(df['artist_top_genre' ]) nclusters = 3 seed = 0 km = KMeans(n_clusters=nclusters, random_state=seed).fit(X) y_cluster_kmeans = km.predict(X) print (y_cluster_kmeans)score = metrics.silhouette_score(X, y_cluster_kmeans) print (score)
[2 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 0 2 1 1 2 2 2 0
2 0 1 2 2 2 0 1 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 2 0 2 1 0 2 0 1 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 1
0 2 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 2 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 1 2 0 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 2 1 2 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 2 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0
2 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 2 1 1 1 1 1 0
1 1 1 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
1 2 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1
2 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 2 1 1 2 2 2 0 2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 2 1 1 2 1 0 2 2 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 0 2 0 2 1 1 2 2 2 0 0 2 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 2 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 1 2 1 0 0 0 2 2 2 0 2
2 2 0 2 2 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 1 0 2 1 1 1 0 1 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1]
0.5918299843029218
wcss = [] for i in range (1 , 11 ): kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=i, init='k-means++' , random_state=42 ).fit(X) wcss.append(kmeans.inertia_) plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 5 )) sns.lineplot(range (1 , 11 ), wcss, marker='o' , color='red' ) plt.title('Elbow' ) plt.xlabel('Number of clusters' ) plt.ylabel('WCSS' ) plt.show()
D:\Scoop\apps\anaconda3\current\lib\site-packages\sklearn\cluster\_kmeans.py:1036: UserWarning: KMeans is known to have a memory leak on Windows with MKL, when there are less chunks than available threads. You can avoid it by setting the environment variable OMP_NUM_THREADS=3.
warnings.warn(
D:\Scoop\apps\anaconda3\current\lib\site-packages\seaborn\_decorators.py:36: FutureWarning: Pass the following variables as keyword args: x, y. From version 0.12, the only valid positional argument will be `data`, and passing other arguments without an explicit keyword will result in an error or misinterpretation.
warnings.warn(
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=3 ).fit(X) labels = kmeans.predict(X) plt.scatter(df['popularity' ], df['danceability' ], c=labels) plt.xlabel('popularity' ) plt.ylabel('danceability' ) plt.show() correct_labels = sum (y == kmeans.labels_) print ("%d/%d samples were correctly labeled." % (correct_labels, y.size)) print ('Accuracy score: {0:0.2f}' .format (correct_labels / float (y.size)))
93/530 samples were correctly labeled.
Accuracy score: 0.18
sample-2 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.colorsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport sklearn.datasets as dsfrom sklearn.metrics import homogeneity_score, completeness_score, v_measure_score, adjusted_mutual_info_score,\ adjusted_rand_score, silhouette_score from sklearn.cluster import KMeansfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Ddef expand (a, b ): d = (b - a) * 0.1 return a - d, b + d N = 400 centers = 4 data, y = ds.make_blobs(N, n_features=2 , centers=centers, random_state=2 ) data2, y2 = ds.make_blobs(N, n_features=2 , centers=centers, cluster_std=(1 , 2.5 , 0.5 , 2 ), random_state=2 ) data3 = np.vstack( (data[y == 0 ][:], data[y == 1 ][:50 ], data[y == 2 ][:20 ], data[y == 3 ][:5 ])) y3 = np.array([0 ] * 100 + [1 ] * 50 + [2 ] * 20 + [3 ] * 5 ) m = np.array(((1 , 1 ), (1 , 3 ))) data_r = data.dot(m) matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif' ] = ['SimHei' ] matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus' ] = False cm = matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(list ('rgbm' )) data_list = data, data, data_r, data_r, data2, data2, data3, data3 y_list = y, y, y, y, y2, y2, y3, y3 titles = '原始数据' , 'KMeans++聚类' , '旋转后数据' , '旋转后KMeans++聚类' ,\ '方差不相等数据' , '方差不相等KMeans++聚类' , '数量不相等数据' , '数量不相等KMeans++聚类' model = KMeans(n_clusters=4 , init='k-means++' , n_init=5 ) fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8 , 9 ), facecolor='w' ) for i, (x, y, title) in enumerate (zip (data_list, y_list, titles), start=1 ): ax = fig.add_subplot(4 , 2 , i) plt.title(title) if i % 2 == 1 : y_pred = y else : y_pred = model.fit_predict(x) print (i) print ('Homogeneity:' , homogeneity_score(y, y_pred)) print ('completeness:' , completeness_score(y, y_pred)) print ('V measure:' , v_measure_score(y, y_pred)) print ('AMI:' , adjusted_mutual_info_score(y, y_pred)) print ('ARI:' , adjusted_rand_score(y, y_pred)) print ('Silhouette:' , silhouette_score(x, y_pred), '\n' ) ax.scatter(x[:, 0 ], x[:, 1 ], s=10 , c=y_pred, cmap=cm, edgecolors='none' ) ax.grid(b=True , ls=':' ) plt.tight_layout(2 , rect=(0 , 0 , 1 , 0.95 )) plt.suptitle('数据分布对KMeans聚类的影响' , fontsize=18 ) plt.show()
1
Homogeneity: 1.0
completeness: 1.0
V measure: 1.0
AMI: 1.0
ARI: 1.0
Silhouette: 0.616436816839852
2
Homogeneity: 0.9898828240244267
completeness: 0.9899006758819153
V measure: 0.9898917498726852
AMI: 0.9898081557479033
ARI: 0.9933165272203728
Silhouette: 0.6189656317733315
3
Homogeneity: 1.0
completeness: 1.0
V measure: 1.0
AMI: 1.0
ARI: 1.0
Silhouette: 0.5275987244664399
4
Homogeneity: 0.7296158940840607
completeness: 0.7315285272632114
V measure: 0.7305709588584066
AMI: 0.7283397010755561
ARI: 0.6783811042853299
Silhouette: 0.5366236044449266
5
Homogeneity: 1.0
completeness: 1.0
V measure: 1.0
AMI: 1.0
ARI: 1.0
Silhouette: 0.4790725752982868
6
Homogeneity: 0.7449364376693913
completeness: 0.7755445167472191
V measure: 0.7599323988656883
AMI: 0.757903292819801
ARI: 0.7113213508090338
Silhouette: 0.5737260449304202
7
Homogeneity: 1.0
completeness: 1.0
V measure: 1.0
AMI: 1.0
ARI: 1.0
Silhouette: 0.5975066093204152
8
Homogeneity: 0.9776347312784609
completeness: 0.9728632742060752
V measure: 0.975243166591057
AMI: 0.9745709993295113
ARI: 0.9906840043816505
Silhouette: 0.6013877858619149
C:\Users\utsuk\AppData\Local\Temp\ipykernel_28356\867049078.py:57: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: Passing the pad parameter of tight_layout() positionally is deprecated since Matplotlib 3.3; the parameter will become keyword-only two minor releases later.
plt.tight_layout(2, rect=(0, 0, 1, 0.95))
层次聚类 import numpy as npimport matplotlib as mplimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.cluster import AgglomerativeClusteringfrom sklearn.neighbors import kneighbors_graphimport sklearn.datasets as dsimport warningsdef expand (a, b, r ): d = (b - a) * r return a - d, b + d if __name__ == '__main__' : warnings.filterwarnings(action='ignore' , category=UserWarning) np.set_printoptions(suppress=True ) np.random.seed(0 ) n_clusters = 4 N = 400 data1, y1 = ds.make_blobs(n_samples=N, n_features=2 , centers=((-1 , 1 ), (1 , 1 ), (1 , -1 ), (-1 , -1 )), cluster_std=(0.1 , 0.2 , 0.3 , 0.4 ), random_state=0 ) data1 = np.array(data1) n_noise = int (0.1 * N) r = np.random.rand(n_noise, 2 ) data_min1, data_min2 = np.min (data1, axis=0 ) data_max1, data_max2 = np.max (data1, axis=0 ) r[:, 0 ] = r[:, 0 ] * (data_max1 - data_min1) + data_min1 r[:, 1 ] = r[:, 1 ] * (data_max2 - data_min2) + data_min2 data1_noise = np.concatenate((data1, r), axis=0 ) y1_noise = np.concatenate((y1, [4 ] * n_noise)) data2, y2 = ds.make_moons(n_samples=N, noise=.05 ) data2 = np.array(data2) n_noise = int (0.1 * N) r = np.random.rand(n_noise, 2 ) data_min1, data_min2 = np.min (data2, axis=0 ) data_max1, data_max2 = np.max (data2, axis=0 ) r[:, 0 ] = r[:, 0 ] * (data_max1 - data_min1) + data_min1 r[:, 1 ] = r[:, 1 ] * (data_max2 - data_min2) + data_min2 data2_noise = np.concatenate((data2, r), axis=0 ) y2_noise = np.concatenate((y2, [3 ] * n_noise)) mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif' ] = ['SimHei' ] mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus' ] = False cm = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['r' , 'g' , 'b' , 'm' , 'c' ]) plt.figure(figsize=(10 , 8 ), facecolor='w' ) plt.cla() linkages = ("ward" , "complete" , "average" ) for index, (n_clusters, data, y) in enumerate ( ((4 , data1, y1), (4 , data1_noise, y1_noise), (2 , data2, y2), (2 , data2_noise, y2_noise))): plt.subplot(4 , 4 , 4 * index + 1 ) plt.scatter(data[:, 0 ], data[:, 1 ], c=y, s=12 , edgecolors='k' , cmap=cm) plt.title('Prime' , fontsize=12 ) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' ) data_min1, data_min2 = np.min (data, axis=0 ) data_max1, data_max2 = np.max (data, axis=0 ) plt.xlim(expand(data_min1, data_max1, 0.05 )) plt.ylim(expand(data_min2, data_max2, 0.05 )) connectivity = kneighbors_graph(data, n_neighbors=7 , mode='distance' , metric='minkowski' , p=2 , include_self=True ) connectivity = 0.5 * (connectivity + connectivity.T) for i, linkage in enumerate (linkages): ac = AgglomerativeClustering(n_clusters=n_clusters, affinity='euclidean' , connectivity=connectivity, linkage=linkage) ac.fit(data) y = ac.labels_ plt.subplot(4 , 4 , i + 2 + 4 * index) plt.scatter(data[:, 0 ], data[:, 1 ], c=y, s=12 , edgecolors='k' , cmap=cm) plt.title(linkage, fontsize=12 ) plt.grid(b=True , ls=':' ) plt.xlim(expand(data_min1, data_max1, 0.05 )) plt.ylim(expand(data_min2, data_max2, 0.05 )) plt.suptitle('层次聚类的不同合并策略' , fontsize=15 ) plt.tight_layout(0.5 , rect=(0 , 0 , 1 , 0.95 )) plt.show()
降维问题 缺失值比率 import pandas as pdimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plttrain = pd.read_csv("./_data_set/降维问题/train_v9rqX0R.csv" ) a = train.isnull().sum () / len (train) * 100 variable = [] for i in range (0 , 12 ): if a[i] <= 20 : variable.append(train.columns[i]) print (variable)
['Item_Identifier', 'Item_Weight', 'Item_Fat_Content', 'Item_Visibility', 'Item_Type', 'Item_MRP', 'Outlet_Identifier', 'Outlet_Establishment_Year', 'Outlet_Location_Type', 'Outlet_Type', 'Item_Outlet_Sales']
低方差过滤 import pandas as pdimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plttrain = pd.read_csv("./_data_set/降维问题/train_v9rqX0R.csv" ) train['Item_Weight' ].fillna(train['Item_Weight' ].median(), inplace=True ) train['Outlet_Size' ].fillna(train['Outlet_Size' ].mode()[0 ], inplace=True ) print (train.isnull().sum () / len (train) * 100 )numeric = train[[ 'Item_Weight' , 'Item_Visibility' , 'Item_MRP' , 'Outlet_Establishment_Year' ]] var = numeric.var() numeric = numeric.columns variable = [] for i in range (0 , len (var)): if var[i] >= 10 : variable.append(numeric[i]) print (variable)
Item_Identifier 0.0
Item_Weight 0.0
Item_Fat_Content 0.0
Item_Visibility 0.0
Item_Type 0.0
Item_MRP 0.0
Outlet_Identifier 0.0
Outlet_Establishment_Year 0.0
Outlet_Size 0.0
Outlet_Location_Type 0.0
Outlet_Type 0.0
Item_Outlet_Sales 0.0
dtype: float64
['Item_Weight', 'Item_MRP', 'Outlet_Establishment_Year']
代码相关 存储-读取模型 import numpy as npimport sklearn.linear_model as lm import sklearn.metrics as sm import matplotlib.pyplot as mpimport picklex = np.array([[0.5 ], [0.6 ], [0.8 ], [1.1 ], [1.4 ]]) y = np.array([5.0 , 5.5 , 6.0 , 6.8 , 7.0 ]) model = lm.LinearRegression() model.fit(x, y) print ("训练完成." )with open ('linear_model.pkl' , 'wb' ) as f: pickle.dump(model, f) print ("保存模型完成." ) with open ('linear_model.pkl' , 'rb' ) as f: model = pickle.load(f) print ("加载模型完成." ) pred_y = model.predict(x) mp.figure('Linear Regression' , facecolor='lightgray' ) mp.title('Linear Regression' , fontsize=20 ) mp.xlabel('x' , fontsize=14 ) mp.ylabel('y' , fontsize=14 ) mp.tick_params(labelsize=10 ) mp.grid(linestyle=':' ) mp.scatter(x, y, c='blue' , alpha=0.8 , s=60 , label='Sample Points' ) mp.plot(x, pred_y, c='orangered' , label='Regression' ) mp.legend() mp.show()
训练完成.
保存模型完成.
加载模型完成.
Web-app 一 train 一个逻辑回归模型并用 pickle 打包
然后load
import pandas as pdimport numpy as npfrom sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoderfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_reportfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionimport pickleufos = pd.read_csv('./_data_set/web-app/1/ufos.csv' ) ufos = pd.DataFrame({ 'Seconds' : ufos['duration (seconds)' ], 'Country' : ufos['country' ], 'Latitude' : ufos['latitude' ], 'Longitude' : ufos['longitude' ] }) ufos.Country.unique() ufos.dropna(inplace=True ) ufos = ufos[(ufos['Seconds' ] >= 1 ) & (ufos['Seconds' ] <= 60 )] ufos['Country' ] = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(ufos['Country' ]) ufos.head() x = ufos[['Seconds' , 'Latitude' , 'Longitude' ]] y = ufos['Country' ] X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2 , random_state=0 ) model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000 ).fit(X_train, y_train) y_pred = model.predict(X_test) print (classification_report(y_test, y_pred))print ('Predicted labels: ' , y_pred)print ('Accuracy: ' , accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))model_name = './_data_set/web-app/1/ufo-model.pkl' pickle.dump(model, open (model_name, 'wb' ))
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 41
1 0.85 0.47 0.60 250
2 1.00 1.00 1.00 8
3 1.00 1.00 1.00 131
4 0.97 1.00 0.98 4743
accuracy 0.97 5173
macro avg 0.96 0.89 0.92 5173
weighted avg 0.97 0.97 0.97 5173
Predicted labels: [4 4 4 ... 3 4 4]
Accuracy: 0.9702300405953992
model_load = pickle.load(open (model_name, 'rb' )) print (model_load.predict([[50 , 44 , -12 ]]))
[3]
D:\Scoop\apps\anaconda3\current\lib\site-packages\sklearn\base.py:450: UserWarning: X does not have valid feature names, but LogisticRegression was fitted with feature names
warnings.warn(
二 import pandas as pdfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.svm import SVCfrom sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_scorefrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, confusion_matrix, classification_reportdata = pd.read_csv('./_data_set/cuisines_classification/cleaned_cuisines.csv' ) X = data.iloc[:, 2 :] y = data[['cuisine' ]] X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3 ) model = SVC(kernel='linear' , C=10 , probability=True , random_state=0 ) model.fit(X_train, y_train.values.ravel()) y_pred = model.predict(X_test) print (classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
precision recall f1-score support
chinese 0.73 0.68 0.70 242
indian 0.89 0.88 0.88 246
japanese 0.80 0.79 0.79 262
korean 0.82 0.75 0.78 229
thai 0.75 0.88 0.81 220
accuracy 0.79 1199
macro avg 0.79 0.80 0.79 1199
weighted avg 0.80 0.79 0.79 1199
from skl2onnx import convert_sklearnfrom skl2onnx.common.data_types import FloatTensorTypeinitial_type = [('float_input' , FloatTensorType([None , 380 ]))] options = {id (model): {'nocl' : True , 'zipmap' : False }} onx = convert_sklearn(model, initial_types=initial_type, options=options) with open ("./_data_set/web-app/2/model.onnx" , "wb" ) as f: f.write(onx.SerializeToString())
信息论 两点分布信息熵 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plteps = 1e-5 p = np.linspace(eps, 1 - eps, 100 ) h = -(1 - p) * np.log2(1 - p) - p * np.log2(p) plt.plot(p, h, label='Information entropy' , color='red' , lw=3 ) plt.xlabel('Probability' , fontsize=16 ) plt.ylabel('Entropy' , fontsize=16 ) plt.legend(loc='best' , fontsize=16 ) plt.grid(True ) plt.show()
基尼系数与-ln import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as plteps = 1e-4 p = np.linspace(eps, 1 - eps, 100 ) h = -(1 - p) * np.log2(1 - p) - p * np.log2(p) gini = 2 * (1 - p) * p plt.plot(p, gini, 'r-' , lw=3 ) plt.plot(p, h / 2 , 'g-' , lw=3 ) plt.title('Gini(p) / Ln(p)' , fontsize=16 ) plt.xlabel('p' , fontsize=14 ) plt.ylabel('H' , fontsize=14 ) plt.legend(['Gini' , 'Ln' ], loc='best' , fontsize=14 ) plt.show()
借物表 [1] : https://discover304.top/
[2] : 【上海交大】【腾讯】强强联合 机器学习+深度学习
[3] : The Ultimate Guide to 12 Dimensionality Reduction Techniques (with Python codes)
[4] : https://github.com/microsoft/ML-For-Beginners